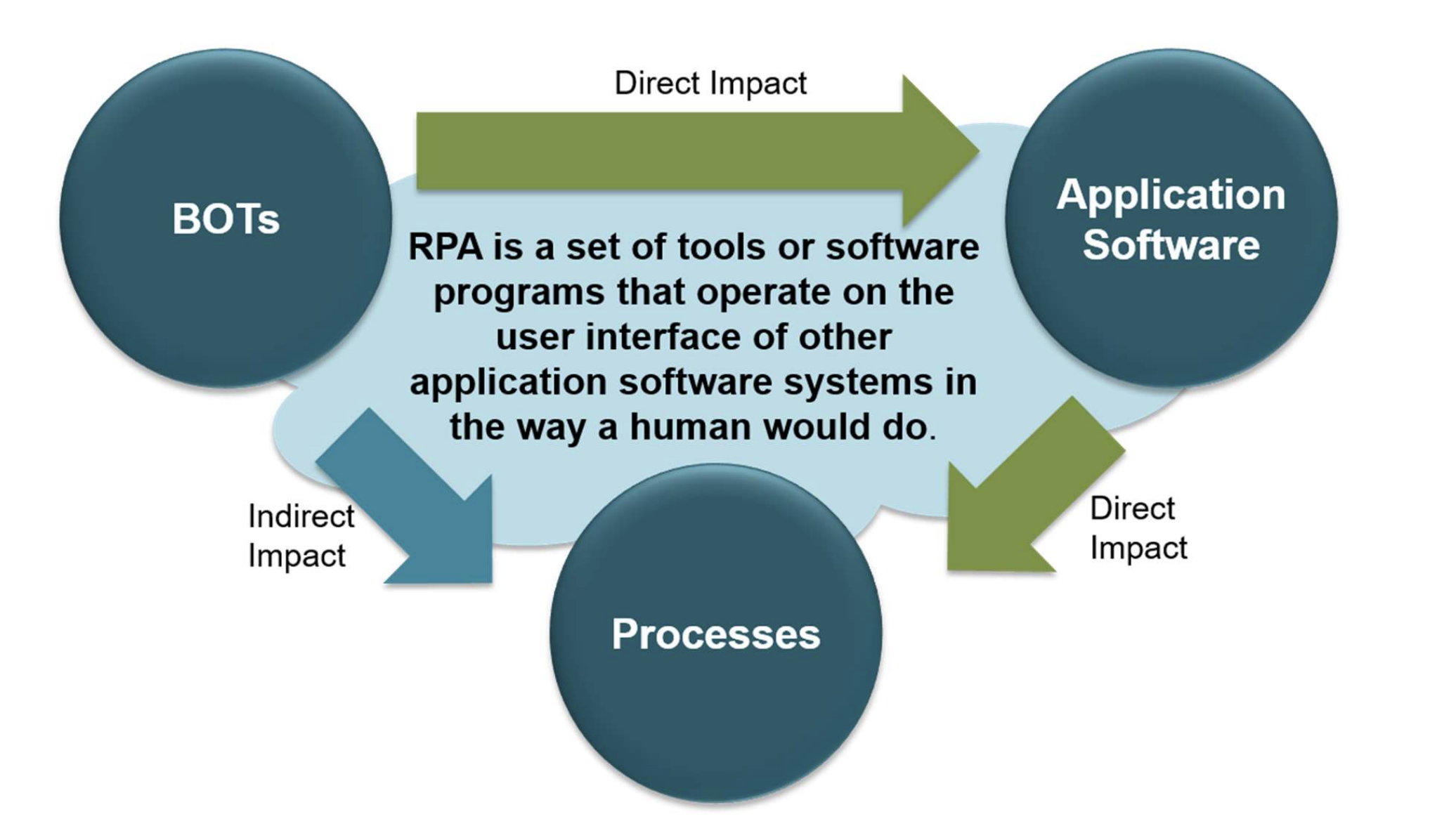
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is rewriting the playbook for enterprise software as we speak. Its primarly concenred with revolutionizing how businesses handle repetitive tasks. By automating mundane, error-prone processes, RPA is delivering not just cost savings but a glimpse of the future—where the lines between day-to-day software and cutting-edge AI blur. At its core, RPA emulates human interaction with software interfaces. It’s not a standalone invention but rather a convergence of AI technologies tailored to automate specific tasks. The burning question, however, isn’t about what RPA is—it’s about what it can automate effectively.
RPA shines in processes that are too infrequent for traditional automation to make financial sense but still repetitive enough to warrant formalization. Think about those tasks that clog up workflows—transferring data between an ERP system and a web application, for instance. By tapping into logs of user interactions or adopting frameworks like Value-Driven RPA, businesses can identify opportunities ripe for automation.
Companies like Telefónica and Xchanging are turning to RPA not just as a productivity hack but as a strategy to streamline operations and drive efficiency.
Value-Driven RPA is more than just a buzzword; it’s a philosophy baked into process-led digital transformation. By leaning on Business Process Management (BPM) capabilities, it maximizes the returns on digital initiatives while minimizing risks. But RPA doesn’t stop at simple task replication. The integration of machine learning and AI—often called Intelligent Process Automation (IPA)—represents its next evolutionary leap.
For IPA to work, though, the groundwork must be laid. That means building datasets designed for machine learning—an effort-intensive but ultimately rewarding step. Once created, these datasets can be shared across similar industries, enabling faster bootstrapping of learning agents. Data collection should focus on tasks where human effort predominates, like user interface interactions (clickstreams, keylogs, etc.). For advanced reinforcement learning solutions, even finer-grained data is needed to reconstruct decision-making patterns and action probabilities.
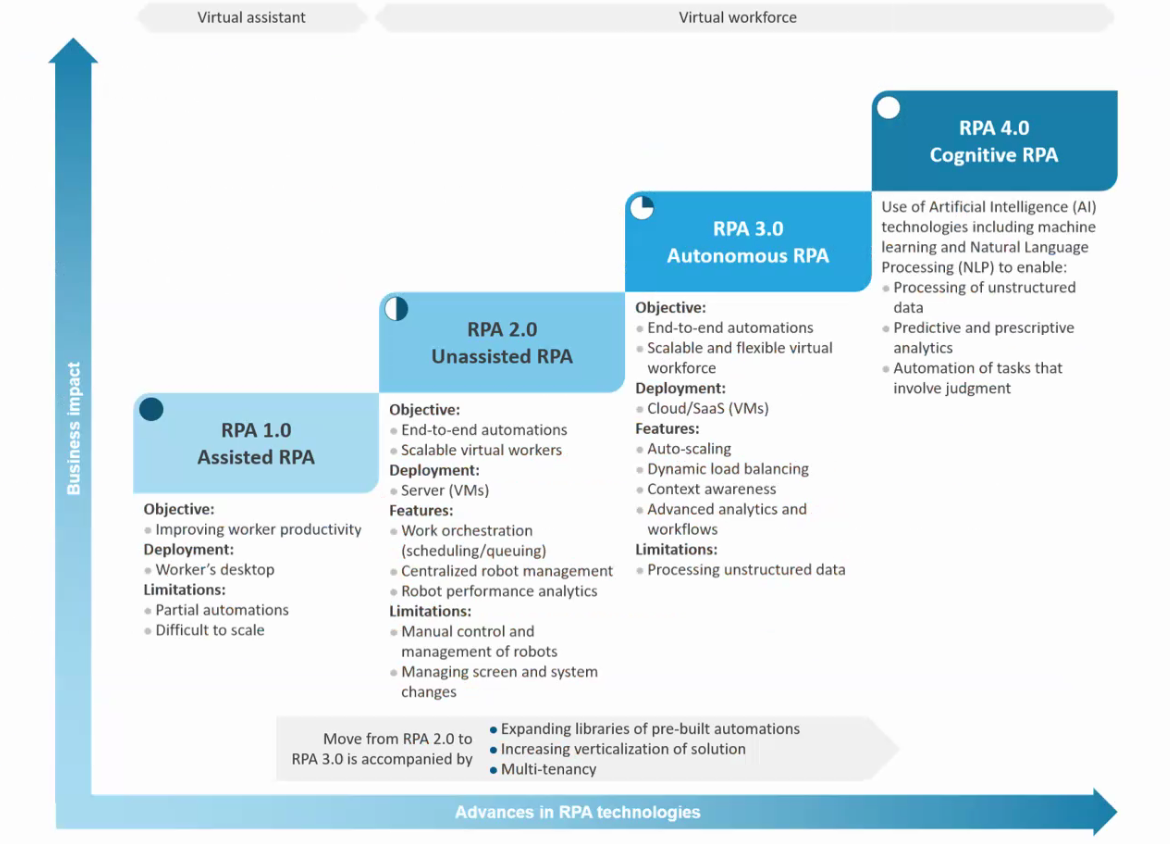
For all its promise, RPA isn’t without hurdles. Exception handling remains a key challenge. Automated systems often falter in the face of unexpected scenarios, and scaling RPA across an organization introduces layers of complexity. By automating human-software interactions and providing decision support, RPA creates new avenues for improving business processes. These tools don’t just complete tasks; they elevate them, offering a strategic edge.
At its best, RPA is about more than automating clicks and keystrokes. It’s about tackling the business processes that are complex—particularly those where human-software interactions that form the backbone of daily operations. From transferring data between systems to providing decision support, RPA is a step toward a smarter enterprise.
The future can be even more exciting but comes with its own set of challenges. Curating enterprise knowledge and leveraging it to reason, plan, and learn is no small feat. These are the frontiers that RPA has yet to conquer. But with every step forward, it reshapes what’s possible, proving that even the mundane can be revolutionary when reimagined through the lens of automation.
Overall RPA represents an interesting shift, one that takes a stab at automating part of business processes which consist of humans interacting with day to day software (e.g giving them transferring data from an ERP system to a web application form). The ability to curate enterprise knowledge and use to reason, plan and learn however are some of the bigger challenges, that still need to be addressed.
References:
[1] Integrating Robotic Process Automation into Business Process Management
[2] Robotic Process Mining: Vision and Challenges
[3] How do Machine Learning, Robotic Process Automation, and Blockchains Affect the Human Factor in Business Process Management?
[4] VALUE-DRIVEN ROBOTIC PROCESS AUTOMATION (RPA) ENABLING EFFECTIVE DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION
